

Within each violin, the white dot represents the median, the boundaries of the thin black rectangle represent the interquartile range, and the black line extending from the rectangle represents 1.5× interquartile range d Schematic of the splicing event types considered (gold, inclusion of intronic sequence blue, exclusion of exonic sequence) e Distribution of splicing events associated with reportable variants by splicing event type ( N = 263 unique transcripts). Importantly, 68 P/LP variants located beyond the consensus splice-site (more than 5 nucleotides from the exon) were identified.Ī Distribution of variant type for variants with classification of VUS, LP, or P ( N = 15,288 reported DNA variants) b Splicing variant classification by nucleotide position ( N = 555 unique splicing variants among 7136 unique total DNA variants) c Violin plots demonstrating the percent spliced index of splicing events associated with variants (P/LP/VUS) in patients ( N = 516 DNA/RNA associated variants), with comparison to their median in healthy donor controls shown in Supplemental Fig. With regards to intronic variants, the vast majority of variants at the well conserved canonical acceptor and donor splice-site (positions −1, −2, and +1, +2 respectively) were classified as P/LP (95.6%). A minority of exonic variants were classified as P/LP (22.7%) and most were classified as VUS (77.3%) however, exonic variants located at the last nucleotide of the exon were more often P/LP (62.7%) due to their impact on splicing. The classification of unique splicing variants ( n = 555 out of 7136 unique total variants) was determined based on their position with respect to the exon (Fig. We found that while missense variants were most observed (69.2% of variants), splicing variants were not rare (6.2%), occurring more than twice as often as copy number variations such as gross deletions/duplications (2.8%) (Fig. A total of 15,288 reported variants, including Pathogenic (P) ( n = 4565), Likely Pathogenic (LP) ( n = 565), and Variant of Unknown Significance (VUS) ( n = 10,158), were reported in 18 RNA-covered genes (Supplemental Table 1) amongst 12,859 cases.
#Bar to psi conversion full#
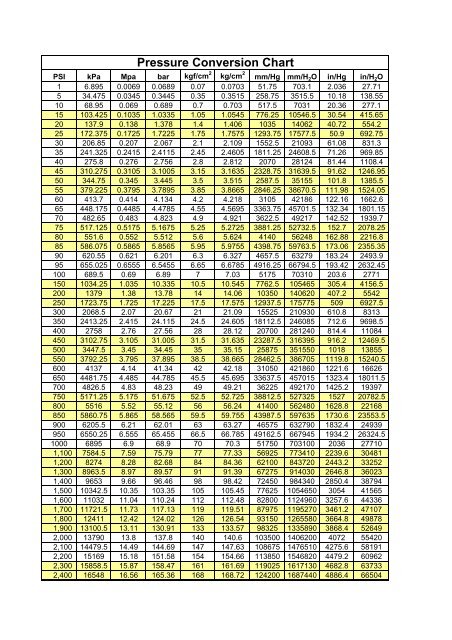
Symbols, abbreviations, or full names for units of length,Īrea, mass, pressure, and other types.In this study, 43,599 tests from 43,524 consecutive individuals who underwent paired DNA-RNA genetic testing from March 2019 through April 2020 were eligible for analysis. You can find metric conversion tables for SI units, as wellĪs English units, currency, and other data. It is the pressure resulting from a force of one pound-force applied to an area of one square inch.Ĭonversion calculator for all types of measurement units. The pound per square inch or, more accurately, pound-force per square inch (symbol: psi or lbf/in² or lbf/in²) is a unit of pressure or of stress based on avoirdupois units.
Its official symbol is "bar" the earlier "b" is now deprecated, but still often seen especially as "mb" rather than the proper "mbar" for millibars. The word bar is of Greek origin, báros meaning weight. The bar is a measurement unit of pressure, equal to 1,000,000 dynes per square centimetre (baryes), or 100,000 newtons per square metre (pascals). Psi to bar, or enter any two units below: Enter two units to convert From: You can do the reverse unit conversion from


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
